Astranis
Founded Year
2015Stage
Series D | AliveTotal Raised
$762.57MLast Raised
$200M | 9 mos agoMosaic Score The Mosaic Score is an algorithm that measures the overall financial health and market potential of private companies.
+44 points in the past 30 days
About Astranis
Astranis specializes in the design, manufacture, and operation of advanced high-orbit satellites within the aerospace industry. The company offers dedicated satellite broadband services through its MicroGEO product, which operates in geostationary orbit and is aimed at providing connectivity for small and medium-sized countries and commercial customers. Astranis also supports government missions with contracts for science, positioning, navigation, and timing services across various orbits. It was founded in 2015 and is based in San Francisco, California.
Loading...
ESPs containing Astranis
The ESP matrix leverages data and analyst insight to identify and rank leading companies in a given technology landscape.
The satellite internet service providers (ISPs) market offers a compelling solution for customers who require reliable and accessible internet connectivity in areas where traditional terrestrial networks are limited or unavailable. By utilizing a network of satellites orbiting the earth, satellite ISPs offer a global reach, enabling connectivity in remote locations, rural areas, and even on moving…
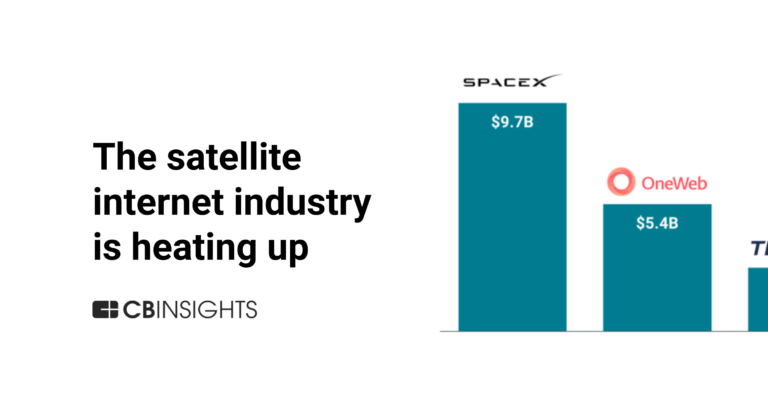
Astranis named as Challenger among 14 other companies, including SpaceX, Viasat, and Iridium Communications.
Loading...
Research containing Astranis
Get data-driven expert analysis from the CB Insights Intelligence Unit.
CB Insights Intelligence Analysts have mentioned Astranis in 1 CB Insights research brief, most recently on Jun 6, 2023.
Expert Collections containing Astranis
Expert Collections are analyst-curated lists that highlight the companies you need to know in the most important technology spaces.
Astranis is included in 3 Expert Collections, including Unicorns- Billion Dollar Startups.
Unicorns- Billion Dollar Startups
1,270 items
Sales & Customer Service Tech
600 items
Companies offering technology-driven solutions to enable, facilitate, and improve customer service across industries. This includes solutions pre-, during, and post-purchase of goods and services.
Aerospace & Space Tech
4,619 items
These companies provide a variety of solutions, ranging from industrial drones to electrical vertical takeoff vehicles, space launch systems to satellites, and everything in between
Astranis Patents
Astranis has filed 5 patents.
The 3 most popular patent topics include:
- satellite broadcasting
- antennas (radio)
- communications satellites
Application Date | Grant Date | Title | Related Topics | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
6/12/2023 | 6/11/2024 | Satellite broadcasting, Radio frequency antenna types, Communications satellites, Antennas (radio), Network topology | Grant |
Application Date | 6/12/2023 |
|---|---|
Grant Date | 6/11/2024 |
Title | |
Related Topics | Satellite broadcasting, Radio frequency antenna types, Communications satellites, Antennas (radio), Network topology |
Status | Grant |
Latest Astranis News
Apr 9, 2025
SpaceNews Search Home / Q&A: Swissto12 CEO Emile de Rijk explains why he thinks the market is shifting his way Q&A: Swissto12 CEO Emile de Rijk explains why he thinks the market is shifting his way Swissto12 CEOEmile de Rijk founded the company in 2011 with a focus on RF subsystems before scaling to full satellites. Credit: Swissto12 Colorado Springs — The commercial geostationary (GEO) satellite market is undergoing rapid transformation. Operators are adapting to shrinking broadcast revenues, increased pressure from low Earth orbit (LEO) constellations and the demand for more flexible, cost-effective solutions. In the past, the GEO industry competed for 15-20 commercial communications satellite orders annually with each vehicle typically the size of a school bus and weighing several tons. But just six commercial GEO comsat orders were placed in 2024, according to Novaspace — the lowest number in two decades. Half of those were for small GEO satellites. This shift is creating new opportunities for companies like 3D printing specialist Swissto12, which is set to deploy its first 1,000-kilogram GEO spacecraft next year for Intelsat. The Swiss company is part of a growing cohort of small GEO specialists, including Astranis, which builds even smaller platforms. Swissto12 CEO Emile de Rijk believes this new class of satellites will unlock previously invisible market demand and push GEO orders beyond historic highs within five years. In an interview, he discussed how evolving business cases — from secure national connectivity to targeted broadband services — are reshaping procurement strategies, the competitive dynamics in the small GEO segment and what to expect from the market this year and beyond. He spoke recently with SpaceNews’ Jason Rainbow. How do you see the evolving business case for GEOs influencing procurement decisions this year? Emile de Rijk: There are two items challenging the legacy business cases for GEO operators: First, the single-digit decline every year in broadcast revenues, which remains an important part of their business but demand is not enough to justify investing in another large satellite with a lot of channels. There is still a way to position a profitable asset there, if the satellite can be smaller with fewer channels and proportionally lower costs. Sign up for The China Report Beginning this spring, Andrew Jones will be explaining the business, politics and technology in Chinese space activities as part of a new biweekly newsletter. Name(Required) CAPTCHA By submitting this form, you agree to the SpaceNews Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions and to receive email from us. You can opt-out at any time. The other thing is Starlink and other upcoming LEO constellations are challenging the business cases of GEO in the broadband segment. GEO broadband can be competitive compared to LEO, if you look at pure metrics such as capacity, capital expenditure (CapEx) and the extended lifetime of geostationary satellites. But you often have to specialize in secure connectivity, regional markets or different frequency bands that are not offered by the broadband constellations. C-band, for instance, is very valuable in tropical regions; L-band is super valuable for Mobile Satellite Service applications. These use cases are usually smaller than what you would service with a big satellite and more targeted, which also helps reduce risk. Small GEOs offer a more incremental and targeted way of spending CapEx on these business cases to face the realities of how the market is changing. Is there still much of a market for large, legacy GEOs? There remains a strong market for large GEOs. There are business cases that require larger amounts of capacity put into GEO at once, and a small GEO is not going to replace that. I don’t believe in the model where an operator would buy five small GEOs just to replace one big GEO satellite. How does the push for more sovereign, secure connectivity play into this? A lot of nations want to build a pillar of autonomous communications that they fully control and own. A lot of countries don’t need a gigantic military satellite. They need a small, secure connectivity satellite for dual-use applications. Many nations are becoming space-faring, and this will be one of their first acquisitions. If you’re a small country, you’re not going to build your own constellation if it makes no sense. You really want to have one or two GEOs that are very targeted for sovereignty requirements. I think that’s going to be an increasingly large topic for GEO in general and for small GEO in particular. So how many GEO orders do you expect to see this year? My prediction is the market will remain relatively stable for large GEO telecom satellites, but there’s going to be significant growth in the demand for small GEO satellites. And it’s not direct demand for small GEO satellites — it’s demand for business cases that happens to be best addressed with small GEO satellites and is not addressed today, hence not visible in the GEO market. How will that split between large and small GEO satellites evolve? Small GEO is the choice where otherwise the choice would be to do nothing. It is an addition, not a replacement. I think the decline in the GEO orders that we’ve seen is kind of orthogonal to the increase in demand for connectivity. If demand augments, then how come net orders fell? Well, the nature of the demand has evolved, and the current large GEO satellite platforms only address a subset of the demand that’s out there, and there’s an invisible case of demand that has not been addressed until now. Is demand for small GEOs enough to get the total market back to the 15-20 commercial communication orders we used to see a year? If you sum the large GEO and small GEO orders, it will grow and it could even surpass the historic high levels. Some of your rivals offer even smaller GEOs with shorter lifespans. How fierce is the competition in this emerging segment? There are different business models. Some of our competitors also have a capacity leasing model, whereas our customers operate their satellites. So actually, most of the time, we’re not competing. When it comes to the technical solution that others are implementing, there are two different approaches: Trying to take a lower cost, typically LEO bus and upscaling it to GEO, but that usually gets you to a seven-ish year mission instead of 15 years. Then our approach to engineer a small GEO satellite while using a lot of qualified units to find a smart middle ground between heritage from the past and innovative design. Small GEO upstarts are also becoming more mature in the market, which I gather also drives demand. We’re seeing very solid demand and very active proposal activity, with most of the industry operators contacting us about various use cases. A lot of governments are also contacting us with interest in investing in their secure connectivity assets. That being said, it’s about execution. It’s important to still deliver high performance and a reliable product that the operators can count on for the lifetime of their mission. And we’re working toward the typical 15-year lifetime for a GEO mission, which we think is still the right angle. Even if it’s a smaller, lower-cost satellite, it’s still a significant investment for an operator or nation-state that people want to be able to count on. Related
Astranis Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When was Astranis founded?
Astranis was founded in 2015.
Where is Astranis's headquarters?
Astranis's headquarters is located at 575 20th Street, San Francisco.
What is Astranis's latest funding round?
Astranis's latest funding round is Series D.
How much did Astranis raise?
Astranis raised a total of $762.57M.
Who are the investors of Astranis?
Investors of Astranis include Andreessen Horowitz, BlackRock, NTT DoCoMo Ventures, Baillie Gifford, Fidelity and 36 more.
Who are Astranis's competitors?
Competitors of Astranis include SpaceX.
Loading...
Compare Astranis to Competitors

Interstellar Technologies specializes in space transportation services. The company offers convenient services for launching small satellites and has pioneered a vertically integrated rocket-satellite service. It serves the space industry, including commercial spaceflight and satellite services. It was founded in 2013 and is based in Hokkaido, Japan.
Perigee Aerospace is an aerospace technology company that specializes in the development and deployment of space technology solutions. It manufactures orbital launch vehicles. Its vehicle is designed to lift small satellites into low-altitude and high-inclination orbits, which are useful for weather, remote sensing, and imaging satellites. It enables space researchers to send necessary payloads into the orbital atmosphere. The company was founded in 2018 and is based in Daejeon, South Korea.

Exos Aerospace specializes in suborbital space access and operates within the aerospace industry. The company provides launch services using reusable rockets and offers options for orbital transfer and space transportation, utilizing Type 5 carbon composite tanks. It serves sectors that require space access for scientific, educational, and exploratory purposes. It was founded in 2014 and is based in Greenville, Texas.
Orbital ATK is a company focused on aerospace and defense, providing systems and services for space-related applications. The company offers a range of products including space launch vehicles, satellite components, and missile defense systems. Orbital ATK serves various sectors including government and commercial space and defense markets. Orbital ATK was formerly known as Orbital ATK. It was founded in 2015 and is based in Dulles, Virginia. Orbital ATK operates as a subsidiary of Northrop Grumman.

Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) operates in aerospace and defense, providing solutions across different domains. The company focuses on the design, manufacture, and enhancement of aircraft, spacecraft, ground vehicles, and related technologies. SNC's clientele includes government agencies, military organizations, and commercial customers. It was founded in 1963 and is based in Sparks, Nevada.
Roscosmos provides space flights and cosmonautics programs for the Russian Federation. It is based in Moscow, Russian Federation.
Loading...