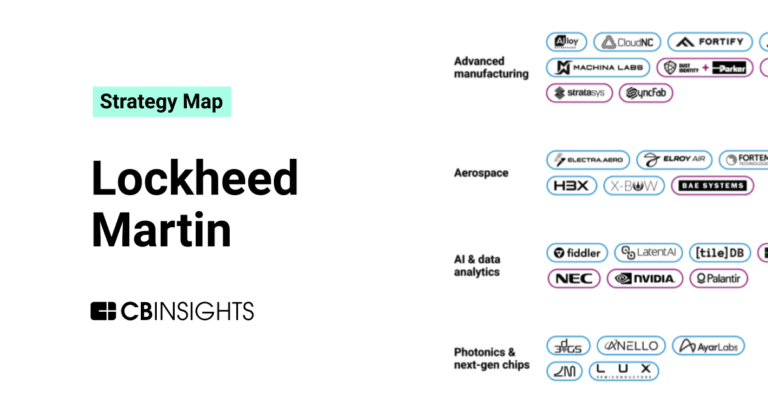
Lockheed Martin
Founded Year
1995Market Cap
101.06BStock Price
430.82Revenue
$0000About Lockheed Martin
Lockheed Martin is a global security and aerospace company focused on the research, design, development, manufacture, integration, and sustainment of advanced technology systems. The company offers a wide range of products and services, including aerospace systems, defense contracting, and cybersecurity solutions, to address the needs of military, government, and commercial clients. Lockheed Martin's offerings encompass various domains such as air, land, sea, space, and cyber, providing integrated solutions and predictive technologies to stay ahead of emerging threats. It was founded in 1995 and is based in Bethesda, Maryland.
Loading...
ESPs containing Lockheed Martin
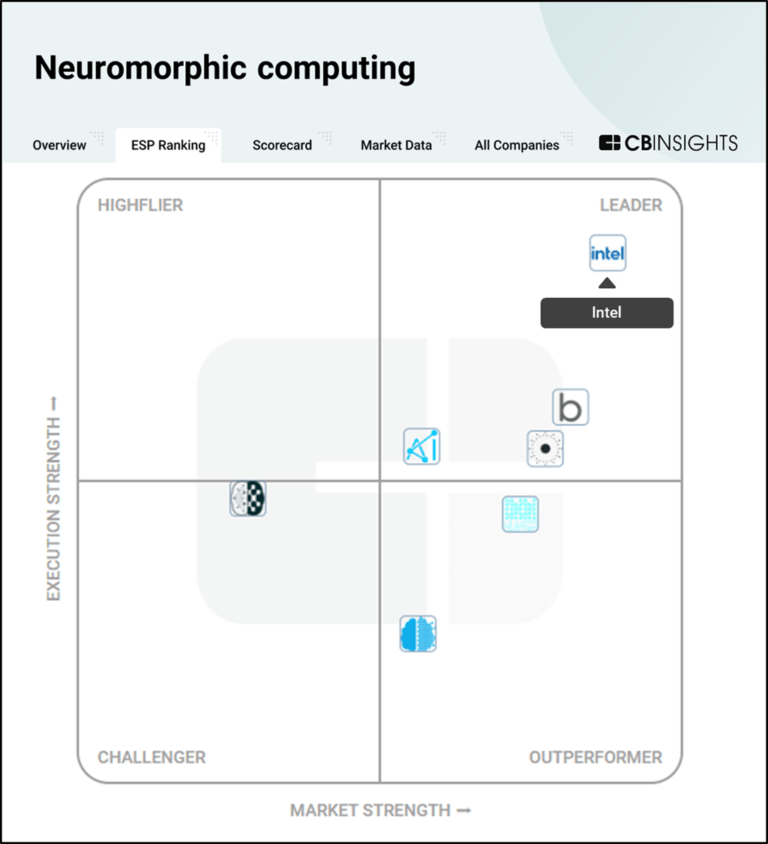
The ESP matrix leverages data and analyst insight to identify and rank leading companies in a given technology landscape.
The mission planning systems (MPS) market focuses on advanced software and hardware solutions to aid military forces in planning, executing, and analyzing missions. These systems, also known as tactical mission systems or military operations planning platforms, combine data from diverse sources such as intelligence reports, geospatial data, and real-time sensor inputs to improve situational awaren…
Lockheed Martin named as Leader among 15 other companies, including BAE Systems, Palantir, and Booz Allen Hamilton.
Loading...
Research containing Lockheed Martin
Get data-driven expert analysis from the CB Insights Intelligence Unit.
CB Insights Intelligence Analysts have mentioned Lockheed Martin in 8 CB Insights research briefs, most recently on Feb 13, 2025.
Feb 13, 2025
The wildfire tech market map
Aug 14, 2024
The AI in defense tech market map

Mar 1, 2024
The satellite & geospatial tech market mapExpert Collections containing Lockheed Martin
Expert Collections are analyst-curated lists that highlight the companies you need to know in the most important technology spaces.
Lockheed Martin is included in 3 Expert Collections, including Fortune 500 Investor list.
Fortune 500 Investor list
590 items
This is a collection of investors named in the 2019 Fortune 500 list of companies. All CB Insights profiles for active investment arms of a Fortune 500 company are included.
Aerospace & Space Tech
4,942 items
These companies provide a variety of solutions, ranging from industrial drones to electrical vertical takeoff vehicles, space launch systems to satellites, and everything in between
Defense Tech
1,067 items
Defense tech is a broad field that encompasses everything from weapons systems and equipment to geospatial intelligence and robotics. Company categorization is not mutually exclusive.
Lockheed Martin Patents
Lockheed Martin has filed 3518 patents.
The 3 most popular patent topics include:
- aerodynamics
- military helicopters
- autogyros
Application Date | Grant Date | Title | Related Topics | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
10/16/2023 | 4/1/2025 | Electrical generators, Thermodynamic cycles, Energy conversion, Thermodynamics, Mechanical power control | Grant |
Application Date | 10/16/2023 |
|---|---|
Grant Date | 4/1/2025 |
Title | |
Related Topics | Electrical generators, Thermodynamic cycles, Energy conversion, Thermodynamics, Mechanical power control |
Status | Grant |
Latest Lockheed Martin News
Apr 8, 2025
Seen here prior to being sealed in its shipping container at Lockheed Martin’s Littleton, Colorado facility, SV08 will join the U.S. Space Force’s operational GPS constellation in orbit. Image: Lockheed Martin. Following the successful accelerated launch of a Global Positioning System on a Falcon 9 rocket in mid-December, the U.S. Space Force, Lockheed Martin and SpaceX are preparing to launch another GPS 3 satellite on a fast tracked basis. The satellite, dubbed GPS 3 Space Vehicle 08 (SV-08), is targeted for launch from Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station no earlier than late May. “This mission represents an outstanding collaboration across multiple teams and agencies,” said U.S. Space Force Col. Andrew Menschner, MD 31 commander, in a statement. “It highlights our ability to rapidly deploy an additional M-Code-capable satellite and continues to push the boundaries of traditional launch timelines.” M-Code stands for “Military Code” and is used to encrypt the signal, allowing government users of the data to know with assurance that they are communicating with the GPS satellite and not a spoof. The Lockheed Martin Global Positioning Satellite (GPS) IIIA, Space Vehicle 08 (SV-08), prepares to be loaded to a U.S. Air Force C-17 Globemaster III from Buckley Space Force Base, Colorado, for transportation to Florida, April 1, 2025. The space vehicle was successfully transferred on April 2, 2025, through a coordinated effort between Lockheed Martin, the U.S. Space Force’s Space Operations Command, and USAF’s Air Mobility Command. Image: U.S. Space Force/Senior Airman Joshua Hollis There are currently 31 GPS satellites on orbit, but the older ones are starting to show their age. During a media briefing on the sidelines of the Space Symposium in Colorado Springs, Colorado, Malik Musawwir, the vice president of Navigation Systems within Lockheed Martin’s National Security Space division, noted that about half of the satellites on orbit are past their designed operating lives. He said the two oldest satellites are about double or triple their originally intended life cycles. “Which means we’re really in a state of borrowed time on some of these vehicles, really increasing the demand to get some of these newer vehicles into the constellation to be able to support this critical mission,” Musawwir said. “GPS underpins every facet of what we do, so we can’t afford to have any downtime.” Musawwir said heading into the launch of GPS 3 SV-07 last year, nicknamed “Sally Ride,” Lockheed Martin had four completed GPS 3 vehicles, which complete that series of satellite. They are working on the next generation, called GPS 3F, which will carry on the number system, beginning with GPS 3 Follow-On (GPS 3F) SV-11. GPS 3 SV-08 now in Florida for processing ahead of its launch in late May. “We’re down to two that we have in Waterton today with the plan to launch remaining two in the next year,” Musawwir said. “So, looking forward to an eventful 2025 of launch activity to really clear out the barn, so to speak.” Lockheed Martin has GPS 3F SV-11, -12 and -13 well into the work flow. GPS 3 SV-13 is currently going through what Musawwir called “core mate.” “You’re taking the equipment panels that contain all the major electronics for the bus and payload and mating that into the propulsion core, the propulsion system. Hence the name ‘core mate,’” he explained. “Our assembly, test and launch operations team is now actively working on space vehicle integration and getting this into what we call ‘single line flow,’ which is where you go through final assembly, final test and into all the environments that you need to run the spacecraft through to ensure that it’s operating as expected.” Musawwir said the GPS 3F satellites have about 60 times more anti-jamming capabilities as compared to the previous generation of GPS satellite. The first of these satellites is expected to launch in 2027. Lockheed Martin is currently on contract to build GPS 3F satellites through SV-20, but they can expand that up to SV-32, upon request. Second swap The GPS 3 SV-08 satellite is nicknamed “Katherine Johnson,” after the mathematician who helped pioneer early human spaceflight with her calculations. The announcement of its launch onboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket marks the second time that the U.S. Space Force’s Space Systems Command decided to shift the launch of a GPS satellite from a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Vulcan rocket to a Falcon 9. Space Systems Command confirmed that the launch in December of GPS 3 SV-07 on a Falcon 9 didn’t mean that ULA would lose out on a future launch. A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket cruises by a nearly full Moon during the RRT-1 mission on Monday, Dec. 16, 2024. Image: Michael Cain/Spaceflight Now “This launch executes a launch vehicle trade of the GPS 3-7 mission from Vulcan to a Falcon 9 rocket, and swaps a later GPS 3F-1 mission from Falcon Heavy to Vulcan, showcasing our ability to launch in three months, compared to the typical 24 months,” said USSF Col. Jim Horne, senior materiel leader of Launch Execution for AATS in a statement. “It highlights another instance of the Space Force’s ability to complete high priority launches on a rapid timescale, which demonstrates the capability to respond to emergent constellation needs as rapidly as Space Vehicle readiness allows.” For the shift with GPS 3 SV-08, Space Systems Command hasn’t announced if there will be another swap of missions to add a different GPS flight for Vulcan. During a media roundtable on Monday, ULA President and CEO Tory Bruno said it wasn’t necessarily unusual for the government to swap missions with launch providers. “I think you will see, just as we’ve seen in the past, occasionally a mission is reassigned from us to them and from them to us,” Bruno said. Bruno said as the main provider for launch services as part of the National Security Space Launch (NSSL) Phase 2 contract, they were assigned about 60 percent of the missions across the five order years of launch assignments. But he said ULA is very aware that sometimes things need to be shifted and that call is up to the U.S. Space Force. United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket sits at launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) ahead of the planned Cert-2 launch on Oct. 4, 2024. Image: Adam Bernstein/Spaceflight Now He added, without going into classified detail, that there are unique aspects that apply to GPS 3 satellites that didn’t apply necessarily to their predecessors. “They are different than the GPS 2 spacecraft. They are jam-resistant, they have military capabilities that are not present [in older versions],” Bruno said. “So, the government has a specific use in mind for them and they have that for all of their spacecraft. And sometimes that changes and they’ll either push back or pull one ahead. “And then they’ll look at their contractors and what capabilities exist at the moment and what space is available on the manifest and they’ll make decisions. And they’ll move them around. They’re generally very transparent when they do that with us and they try really, really hard to be fair. We’re ok with that.” Asked why the mission was moved from the Vulcan rocket to the Falcon 9, Bruno deferred to the Space Force on that. Spaceflight Now reached out to Space Systems Command for clarification on this and we’re waiting to hear back.
Lockheed Martin Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When was Lockheed Martin founded?
Lockheed Martin was founded in 1995.
Where is Lockheed Martin's headquarters?
Lockheed Martin's headquarters is located at 6801 Rockledge Drive, Bethesda.
Who are Lockheed Martin's competitors?
Competitors of Lockheed Martin include Novatron, Firestorm, Blue Origin, Triumph Group, Tekever and 7 more.
Loading...
Compare Lockheed Martin to Competitors
Metrea provides solutions to national security problems by facilitating commercial business models to unleash innovation cycles that anticipate emerging threats. The company offers solutions for air, electromagnetic, space, and simulation. The company was formerly known as Meta Aerospace. The company was founded in 2016 and is based in Washington, DC.
Safran is a company that focuses on aviation and operates in the aerospace and defense industries. The company provides a range of products and services including aircraft equipment such as landing gear, wheels, brakes, and avionics, as well as aircraft interiors and propulsion systems. Additionally, Safran offers defense systems and equipment, and has expertise in space technologies, particularly in rocket propulsion systems and high-performance space optics. It is based in Paris, France.

U.S. Department of Defense focuses on national security and defense. Its main functions include maintaining military forces to deter war and ensuring the security of the nation through various means, including global partnerships. The department also supports a significant civilian workforce and provides services to veterans and military families. It was founded in 1949 and is based in Washington, DC.
Raytheon Intelligence & Space is a company that focuses on the development of disruptive technologies in the defense and aerospace industry. The company's main offerings include advanced sensors, training programs, and cyber and software solutions that provide a decisive advantage to civil, military, and commercial customers. These services primarily cater to the defense and aerospace industry. It was founded in 2020 and is based in Arlington, Virginia.
DSO National Laboratories is a national defense research and development organization in Singapore, focusing on developing technological innovations to enhance defense capabilities. The organization offers services from research to systems development, creating technologies and solutions for Singapore's defense needs. DSO National Laboratories explores and invests in emerging technologies to ensure future-ready defense and security capabilities. It was founded in 1972 and is based in Singapore, Singapore.

CX2 operates as a defense technology company that develops hardware and software platforms to detect, disrupt, and defend the electromagnetic spectrum for military applications. The company provides solutions for the defense sector, particularly in the areas of unmanned systems and electronic warfare. It was founded in 2024 and is based in El Segundo, California.
Loading...